Struggling to understand how a transmission works? It's a complex system, and bad information can lead to costly mistakes. I'm here to simplify it for you.
A car transmission1's main parts are the gears2, shafts, clutch3 (manual) or torque converter4 (automatic), and synchronizers5. They work together to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, allowing you to control speed and torque.
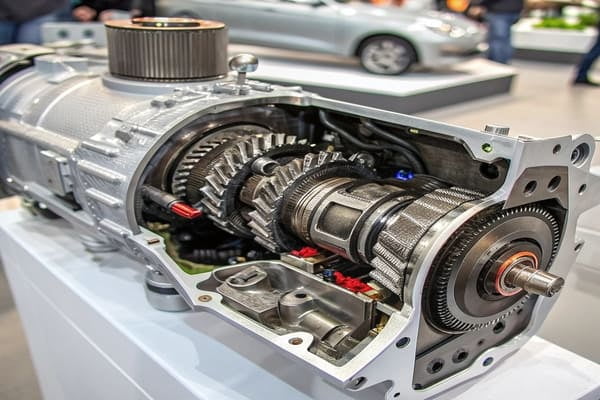

Now that you have a basic idea, let's look closer. Understanding these parts is key for anyone in the auto industry, from manufacturing to repair. Let me guide you through the details.
What Is a Car Transmission System and Why Is It Essential?
Does your vehicle feel sluggish or unresponsive? The transmission might be the issue. Understanding its role is the first step to diagnosing problems and ensuring optimal performance.
A transmission is a gearbox that uses gears2 to change the engine's speed and torque before sending power to the wheels. It's essential because engines operate best within a narrow RPM range6, and the transmission makes sure the wheels get the right power for any driving condition.
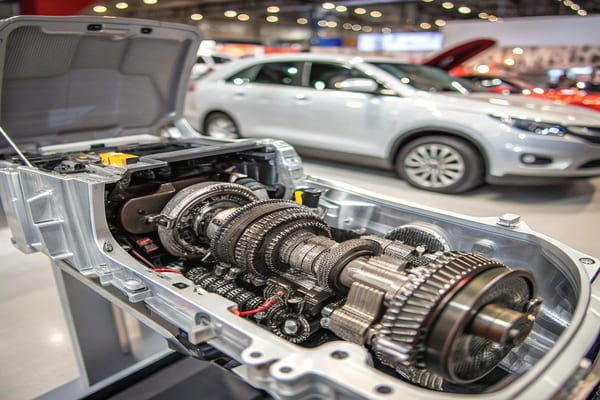

Dive Deeper
A car's engine generates power most efficiently at certain speeds (RPMs). However, your car's wheels need to turn at many different speeds. The transmission is the critical link between them. It’s like the gears2 on a bicycle. When you start pedaling or go uphill, you use a low gear to make pedaling easier (more torque). When you’re on a flat road, you shift to a high gear to go faster without pedaling furiously.
A car transmission1 does the same thing.
The Role of Torque and Speed
In low gears2, the transmission multiplies the engine's torque. This gives you the power to start from a standstill or climb a steep hill. In high gears2, it allows the wheels to spin faster for a given engine speed, improving fuel economy7 during highway cruising. It's all about finding the right balance between power and speed for the situation.
Why Precision Matters in Manufacturing
Getting this system to work smoothly is incredibly difficult. I remember when we first started producing transmission assemblies. The precision required is on another level. Standard assembly equipment just can't meet the required tolerances. The gear mesh clearance8, for example, is one of the hardest things to get right. If it's off by even a tiny amount, the transmission will be noisy or shift poorly. We learned that the hard way, and it’s why we now use highly specialized machinery for these jobs.
What Are the Different Types of Car Transmissions Available Today?
Confused by terms like CVT, DCT, and automatic? Choosing the wrong transmission type for your product line can alienate customers. Let's clear up the confusion.
The main types are Manual (MT), Automatic (AT), Continuously Variable (CVT), and Dual-Clutch (DCT). Each offers different driving feels, efficiency levels, and performance characteristics9. Choosing the right one depends on the vehicle's purpose and target market.
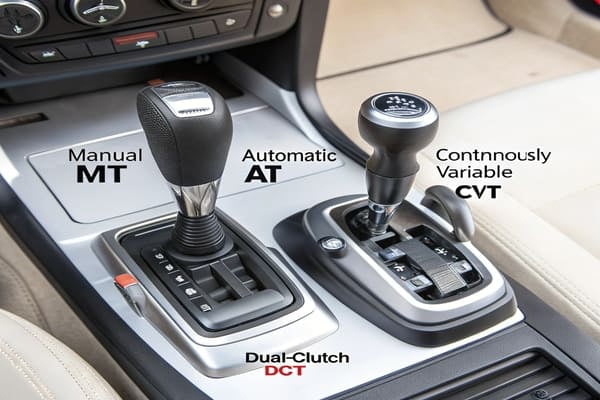
Dive Deeper
Each transmission type offers a unique experience and has its own manufacturing complexities. In our B2B business, we've developed components for all of them, and each presents a different challenge.
Manual Transmission (MT)
This is the classic "stick shift." It gives the driver full control over gear changes using a clutch3 pedal and a gear selector10. It's known for being engaging to drive and very reliable due to its simpler mechanical design.
Automatic Transmission (AT)
This is the most common type. It uses a torque converter4 and planetary gears2ets to change gears2 automatically. It’s convenient for daily driving, especially in traffic.
Continuously Variable Transmission11 (CVT)
A CVT doesn't have fixed gears2. Instead, it uses a system of belts and pulleys to provide a seamless range of gear ratios. This results in very smooth acceleration and excellent fuel efficiency, but some drivers don't like the way it feels.
Dual-Clutch Transmission12 (DCT)
A DCT is like two manual transmission13s in one. One clutch3 controls the odd-numbered gears2, and the other controls the even ones. This allows for lightning-fast gear changes and provides a very sporty feel. The control modules for a DCT are far more complex than for a traditional automatic.
Here is a simple breakdown:
| Transmission Type | Driver Involvement | Fuel Efficiency | Performance Feel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual (MT) | High | Good | Engaging |
| Automatic (AT) | Low | Moderate | Smooth |
| CVT | Low | Excellent | Very Smooth |
| DCT | Low (but sporty) | Very Good | Fast & Sporty |
What Is a Clutch and What Are Its Main Components?
Grinding noises when you shift gears2 in a manual car? Your clutch3 might be failing. Ignoring it leads to bigger, more expensive transmission damage.
A clutch3 is a mechanical device found in manual transmission13s that engages and disengages the power flow from the engine to the gearbox. Its main parts are the flywheel, clutch3 disc, pressure plate, and release bearing.
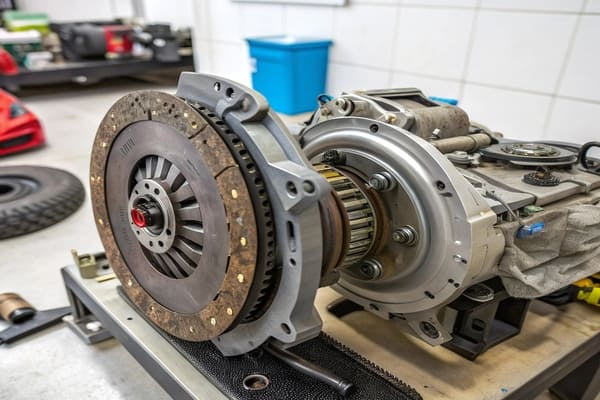

Dive Deeper
The clutch3 is what makes shifting gears2 possible in a manual transmission13. When you press the clutch3 pedal, you're temporarily disconnecting the engine from the transmission so you can select a new gear without grinding anything.
Here’s how the main components work together:
- Flywheel: This is a heavy disc attached to the engine's crankshaft. It provides a smooth surface for the clutch3 to connect to.
- Clutch Disc: This is a disc with friction material on both sides. It's connected to the transmission's input shaft.
- Pressure Plate: This is a spring-loaded plate that bolts to the flywheel. Its job is to clamp the clutch3 disc firmly against the flywheel, connecting the engine to the transmission.
- Release Bearing: When you press the clutch3 pedal, this bearing pushes against the pressure plate, releasing the clamping force. This allows the clutch3 disc to spin freely, disconnecting the engine.
I'll never forget an early project with a client from Pakistan. We were new to full transmission assemblies. Calibrating the gear shift synchronizers14s](https://www.reddit.com/r/explainlikeimfive/comments/124d2j1/eli5_how_do_synchronizers_in_a_manual/)%%%FOOTNOTE_REF_5%%%, which work with the clutch3 to smooth out shifts, was very tricky. You have to open the housing to adjust them, which makes it hard to get the gear engagement just right. The first batch we made had a noticeable "shift shock"—it was a bit clunky. I was worried, but the client actually preferred that aggressive, mechanical feel. It was a lucky break and a huge learning experience. Since then, we've perfected our calibration process to achieve any desired shift feel.
How Does a Torque Converter Work and What Are Its Parts?
Does your automatic car creep forward when you're stopped in "Drive"? That's the torque converter4 at work. Understanding it is key to automatic transmission15 performance.
A torque converter4 is a fluid coupling used in automatic transmission15s instead of a mechanical clutch3. It transfers power from the engine to the transmission using fluid. Its main parts are the impeller, turbine, and stator.
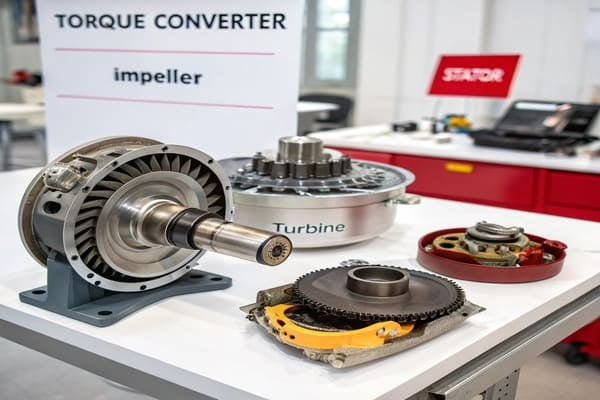

Dive Deeper
Think of a torque converter4 like two fans facing each other. If you turn one fan on (the engine side), the air it blows will start to spin the other fan (the transmission side). A torque converter4 does the same thing, but with transmission fluid instead of air because fluid is much more powerful.
The Impeller and Turbine
The impeller (or pump) is connected to the engine. As the engine runs, the impeller spins and acts like a pump, flinging transmission fluid outward. This fluid hits the blades of the turbine, which is connected to the transmission. The force of the fluid hitting the turbine is what makes it spin, sending power to the wheels.
The Role of the Stator
The stator sits between the impeller and turbine. This is the part that actually multiplies torque. It has specially designed blades that redirect the fluid returning from the turbine. This redirected fluid hits the impeller again, giving it an extra push. This is most effective at low speeds, like when you're accelerating from a stop.
Modern Lock-Up Converters
The precision required to balance a torque converter4 is immense. Any imbalance creates vibrations that can destroy a transmission. We source our high-precision assembly machines from specialized factories in coastal regions like Fujian. We learned that general-purpose machines, like those from Hebei, often can't meet the tight tolerances needed for smooth, reliable operation. Many modern torque converter4s also include a lock-up clutch3. At highway speeds, this clutch3 engages to create a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine and transmission, which eliminates slip and improves fuel economy7.
Conclusion
Understanding transmission parts, from clutch3es to torque converter4s, is crucial for anyone in the auto industry. Proper manufacturing and assembly are key to performance and reliability.
Explore this link to gain a comprehensive understanding of car transmissions and their importance in vehicle performance. ↩
Learn about the role of gears in a transmission system and how they affect vehicle speed and torque. ↩
Discover the function of the clutch in manual transmissions and why it's essential for gear shifting. ↩
Understand the mechanics of a torque converter and its role in transferring power in automatic vehicles. ↩
Find out how synchronizers help in smooth gear shifting and their importance in manual transmissions. ↩
Explore the significance of RPM range in engine performance and how transmissions optimize it. ↩
Learn how different types of transmissions can impact a vehicle's fuel efficiency. ↩
Learn about the importance of gear mesh clearance and how it affects transmission performance. ↩
Get insights into how various transmission types affect vehicle performance and driving experience. ↩
Learn about the gear selector's role in manual transmissions and how it enables gear changes. ↩
Understand the unique features of CVTs and how they differ from traditional transmissions. ↩
Explore the mechanics of DCTs and why they are favored in high-performance vehicles. ↩
Discover the advantages of manual transmissions and why some drivers prefer them over automatics. ↩
Find out how shift synchronizers work to ensure smooth gear changes in manual cars. ↩
Get insights into automatic transmissions and their convenience for everyday driving. ↩
